Cybercriminals deliver IRS tax scams and phishing campaigns by mimicking government vendors
Cybercriminals are leveraging advanced tactics in their phishing-kits granting them a high delivery success rate of spoofed e-mails which contain malicious attachments right before the end of the 2021 IRS income tax return deadline in the U.S. April 18th, 2022 – there was a notable campaign detected which leveraged phishing e-mails impersonating the IRS, and in particular one of the industry vendors who provide solutions to government agencies which including e-mailing, digital communications management, and the content delivery system which informs citizens about various updates.
Cybercriminals purposely choose specific times when all of us are busy with taxes, and preparing for holidays (e.g., Easter), that’s why you need to be especially careful during these times.
The IT services vendor actors impersonated is widely used by major federal agencies, including the DHS, and other such WEB-sites of States and Cities in the U.S. The identified phishing e-mail warned the victims about overdue payments to the IRS, which should then be paid via PayPal, the e-mail contained an HTML attachment imitating an electronic invoice.
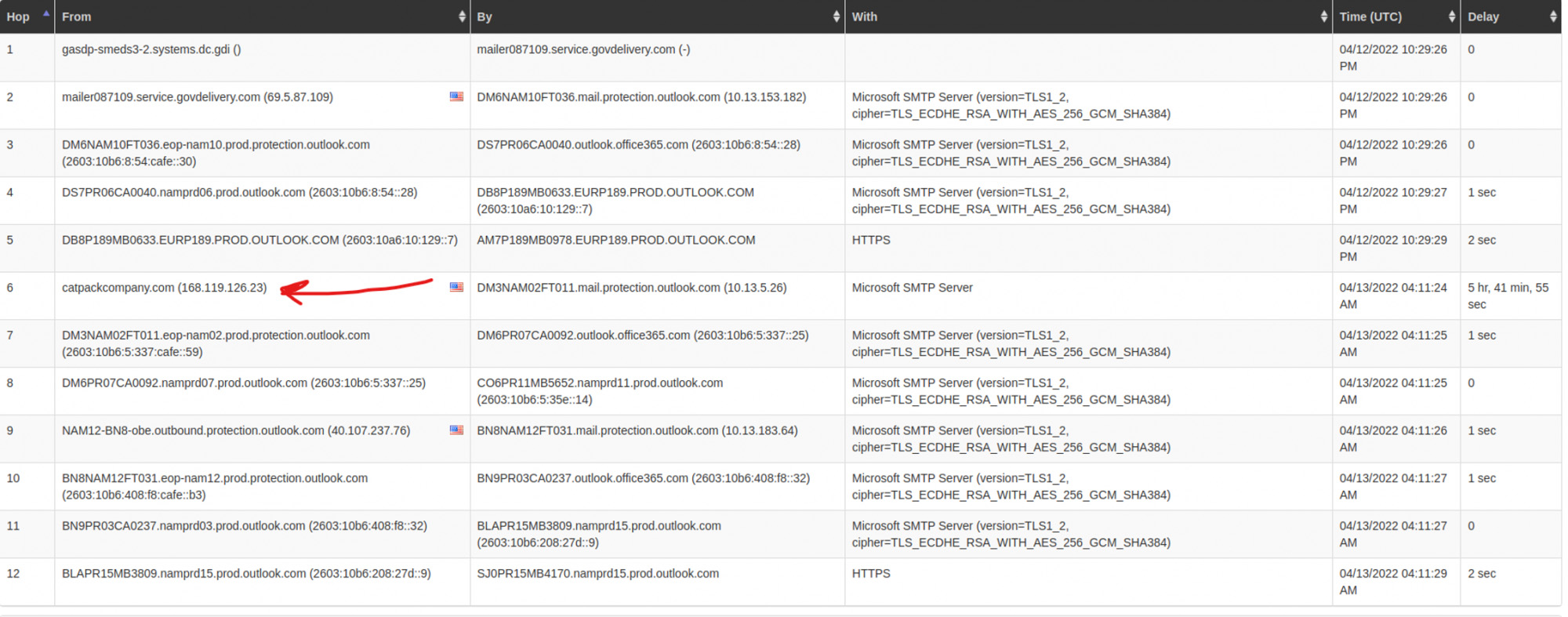
Notably, the e-mail doesn’t contain any URLs, and has been successfully delivered to the victim’s inbox without getting flagged as potential spam. Based on the inspected headers, the e-mail has been sent through multiple “hops” leveraging primarily network hosts and domains registered in the U.S.:
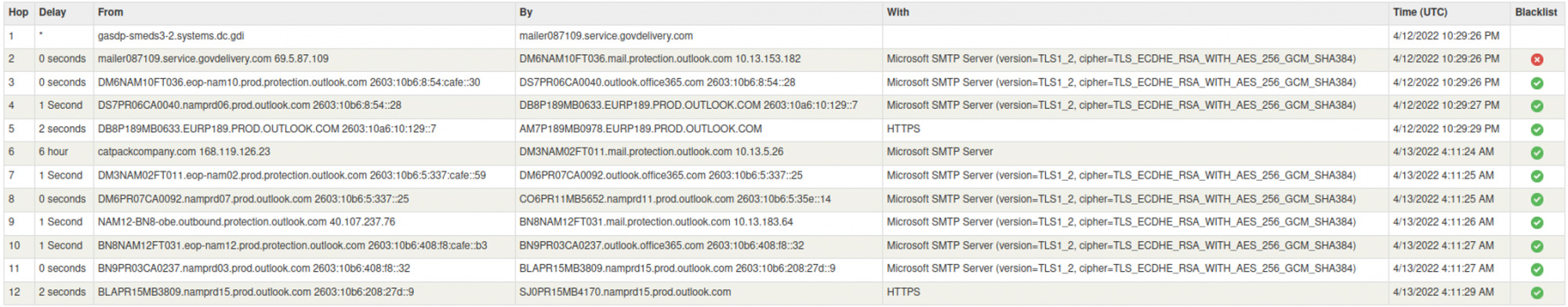
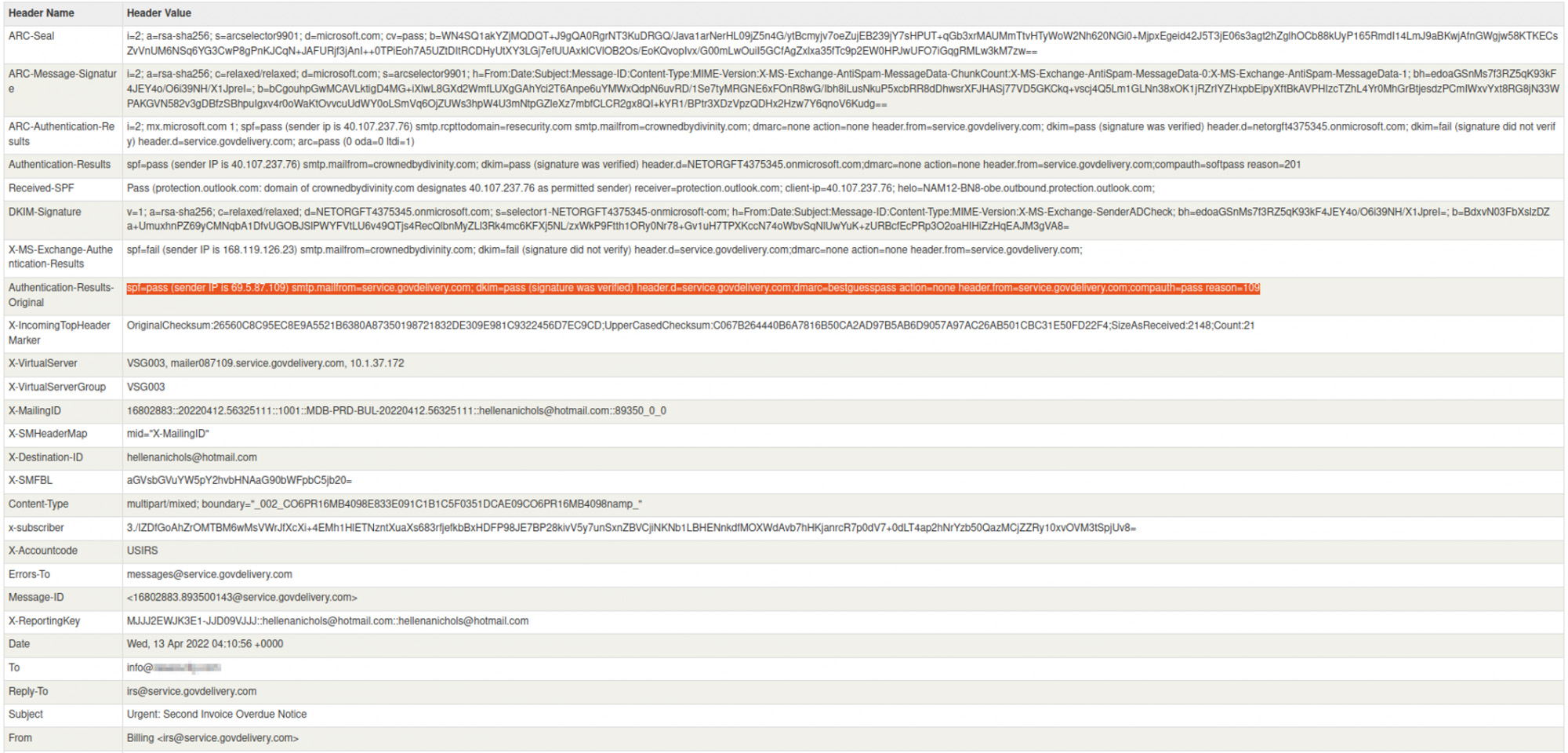
It’s worth noting, on the date of detection none of the involved hosts have previously been ‘blacklisted’ nor have they had any signs of negative IP or abnormal domain reputation:
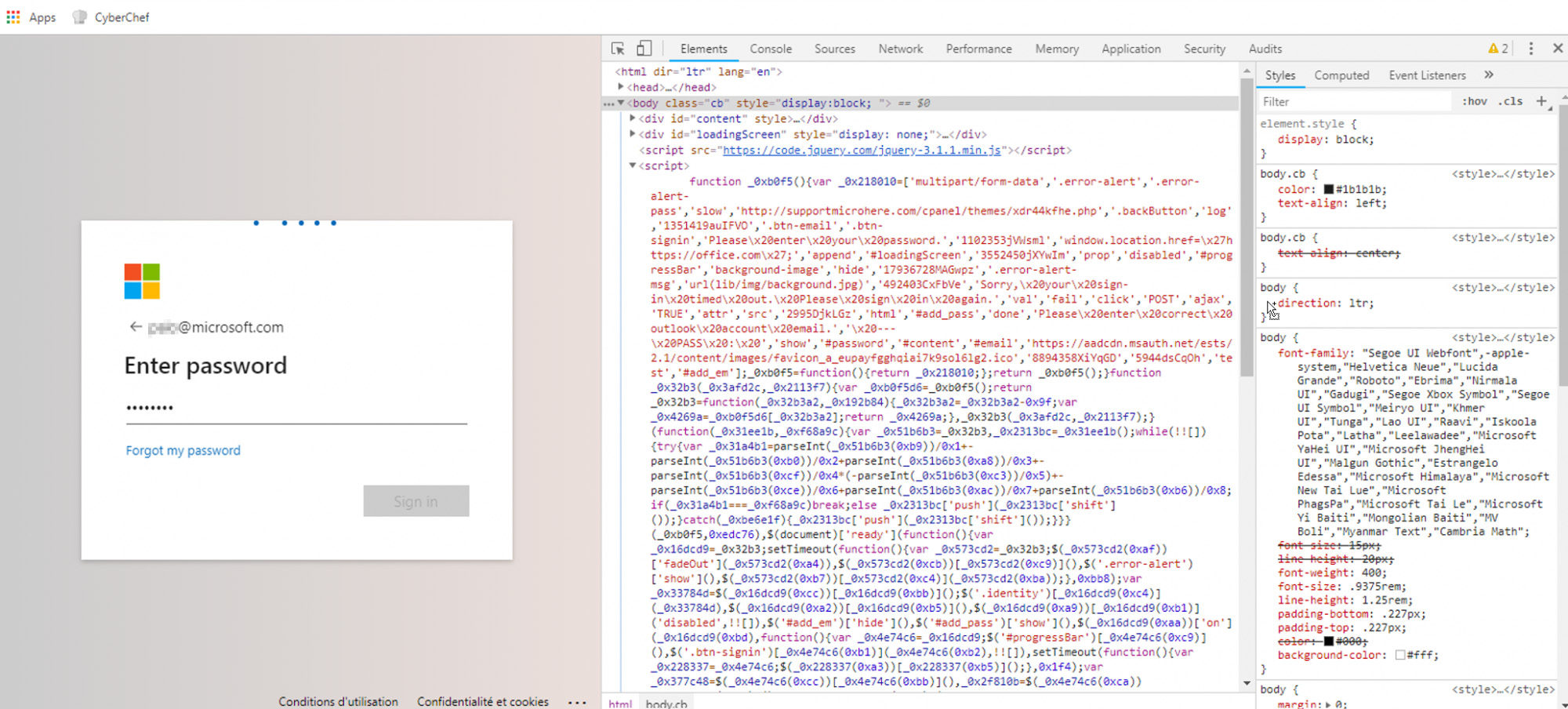
The HTML attachment with the fake IRS invoice contains JS-based obfuscated code.
Further analysis uncovered embedded scenarios detecting the victim’s IP (using GEO2IP module, deployed on a third-party WEB-site), likely done to selectively choose targets or to filter by region.
After the user opens the HTML attachment, the phishing script will encourage the user to enter his credentials, this is done by leveraging an interactive form to impersonate the Office 365 authorization mechanism.
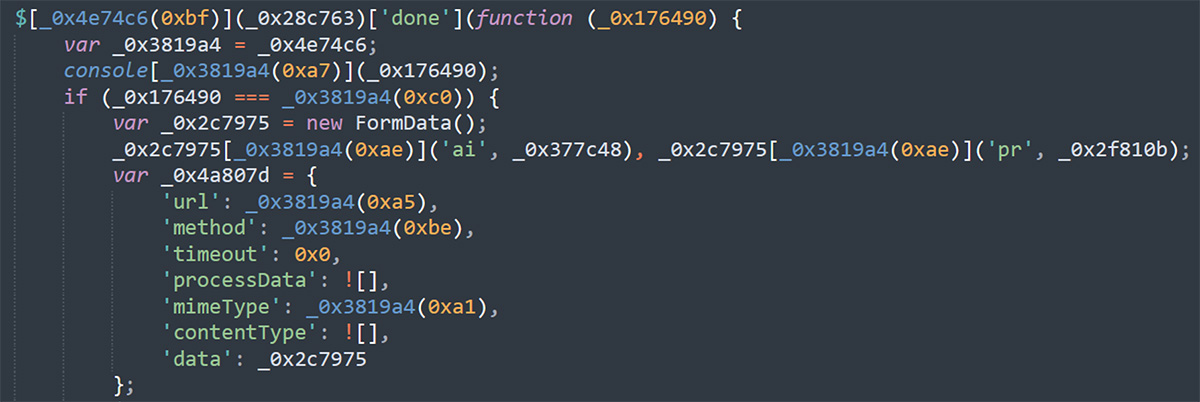
Once the user enters their credentials, the phishing-kit automatically attempts to check access to the victim’s e-mail account via IMAP protocol:
Based on the de-obfuscated JS content the actors were leveraging “supportmicrohere[.]com” domain. Likely, the threat actors attempted to impersonate Microsoft Technical Support and trick user by using the domain with similar spelling.
The script intercepts entered credentials and pass them via POST request:
HTTP POST transmits login and password to script deployed on jbdelmarket[.]com:
The domain jbdelmarket[.]com is hosting a set of scripts to analyze victim’s IP:
The actors log all hosts accessing the phishing page:
Notably, the header of the phishing e-mail contains several domain names with SPF records and DKIM:
Additionally, the attackers leveraged e-mail header fields including X-accountcode (“USIRS”), X-Destination-ID and X-ReportingKey (hellenanichols@hotmail[.]com).
The phishing e-mail also had a Return-Path field defined as another e-mail controlled by the attackers which collects information about unsuccessfully delivered e-mails. The Return-Path is used to process bounces from emails, and it defines how and where bounced emails will be processed.
IOC:
- crownedbydivinity[.]com
- jbdelmarket[.]com
- supportmicrohere[.]com
- hellenanichols@hotmail[.]com
- a9fc34f544eccacf9641f141a830aac9
The Resecurity HUNTER team shared information about the identified phishing campaign with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), Online Fraud Detection and Prevention (OFDP), and the Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration (TIGTA) Hotline. We encourage Internet customers to be especially careful when receiving such e-mails and to validate them first without opening attachments, as it may compromise your digital identity and/or email, and lead to a data theft.
For independent security researchers and cybersecurity community we share a sample of the phishing e-mail caught by our cyber threat intelligence system for further review to increase detection of similar campaigns in future.
References:
- Report Phishing and Online Scams
- Anti-phishing policies in Microsoft 365
- Anti-spoofing protection FAQ