Healthcare industry most common victim of third-party breaches last year
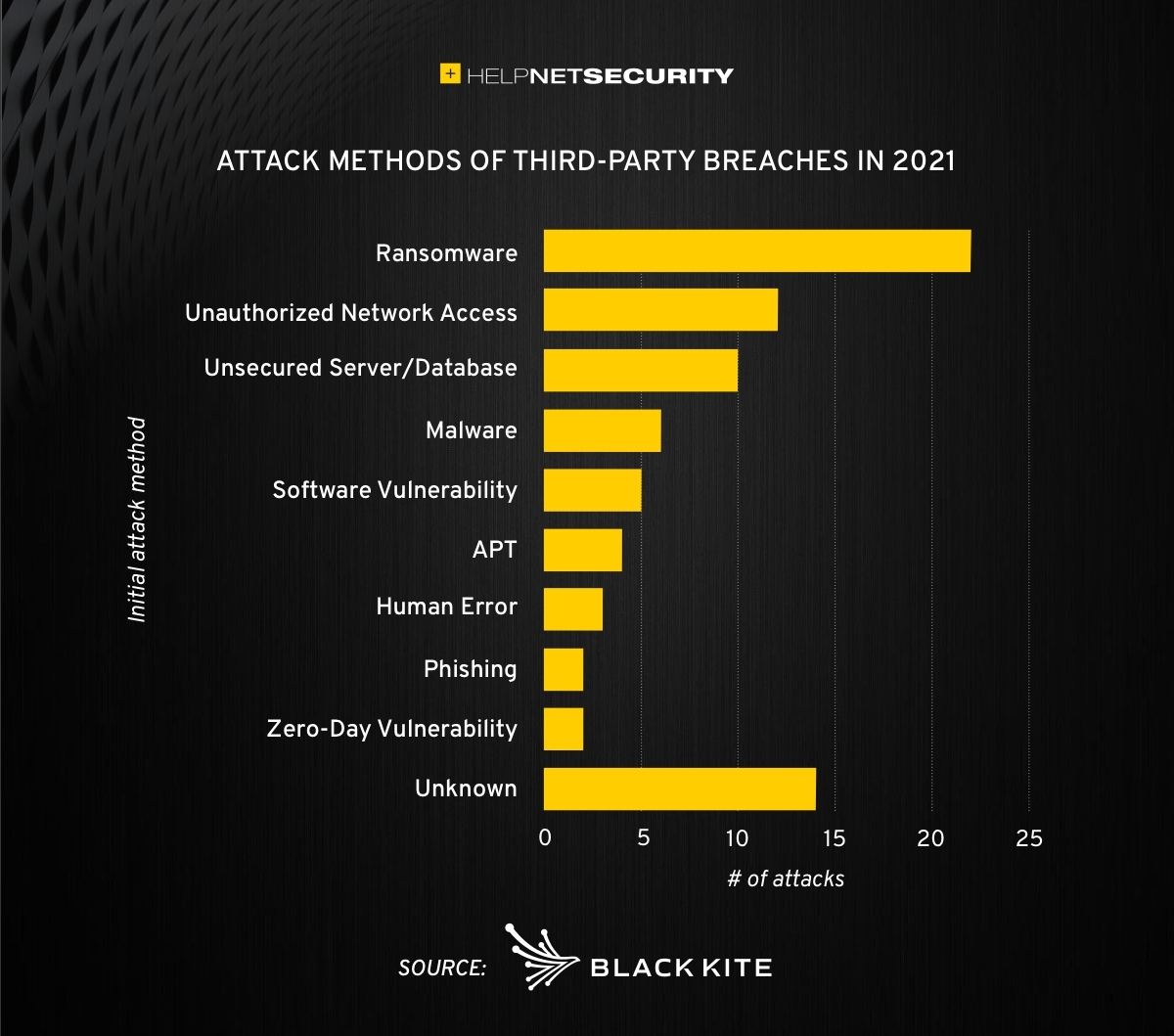
Black Kite released its annual Third-Party Breach Report, which examines the impact of third-party cyber breaches in 2021. Ransomware was the most common attack method behind third-party breaches in 2021, initiating more than one out of four incidents analyzed.
Despite immense cybersecurity improvements following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the healthcare industry was the most common victim of attacks caused by third parties, accounting for 33% of incidents last year. With its rich and diverse personally-identifiable information (PII) data, the government sector accounted for 14% of third party attacks in 2021.
Attackers were able to infiltrate networks and steal data through a variety of methods including exploiting weak passwords and access controls to gain unauthorized network access. Insecure external facing servers and databases also provided easy access to valuable data. Overall, 1.5 billion users’ personally-identifiable information (PII) was leaked as a result of third-party breaches in 2021.
Software publishers most common source of a third-party breach in 2021
Software publishers ranked as the most at-risk vendor for a third consecutive year. Exploitations of software vulnerabilities have led to some of the most notable attacks over the last few years, including the 2020 SolarWinds attack.
“Threat actors have become more agile over the years, particularly with increased ransomware attacks revealing a sense of heightened agility and skill,” said Bob Maley, CSO at Black Kite.
“This is not just a change from 2021, but an overall message. Attack methods are becoming more clever, more detailed, with flexibility and dexterity. If agile attack methods are improving, our response must match, if not counter their growth.”
Kevin Novak, Managing Director, Breakwater Solutions: “By attacking third parties, attackers gain the benefit of hitting an aggregated target; particularly when they can compromise the product being provided by that third party…a software package that then gets distributed to end-users for instance. It’s no wonder why the supply-chain vector has increased so broadly as a preferred target of cyber-attacks. Suppliers are data rich and have significant impetus to pay ransoms lest they lose customers who are paying for their services to remain online and for their data to remain secure.”
“While it is certainly the case that some ransomware attacks are all about ransom and quick returns, a sizeable percentage of ransomware attacks have a more protracted lifecycle that includes deployment of a ransomware across the enterprise, but also includes other objectives too. In these cases, attackers will attempt to find opportunities to commit fraud or exfiltrate data, leaving ransomware as a final parting gift.”
“Whereas ransomware, phishing, unauthorized network access, malware (ransomware being a type), zero-day vulnerabilities, etc., are all methods, these attacks are not all perfectly detached from one another. A phishing attack may lead to unauthorized network access, which might lead to discovery and exploitation of a zero-day vulnerability, that leads to account compromise, that finally give an attacker the ability to deploy ransomware throughout the organization. Sometimes there are fewer steps in the process (phishing that self-propagates ransomware enterprise-wide), but this often isn’t the case.”
Aimei Wei, CTO, Stellar Cyber: “Our findings align with what the report discovered. Organizations have never adopted third party software at today’s speed due to the huge productivity improvement or the enablement brought in by this software. With the benefits comes the security threat from the increased attack surface. It is very challenging to ensure each one of them is vulnerability free, especially with the dynamic software upgrade, it is not future proof even if a software is vulnerability free today. The more practical way to fight this battle is to have a security monitoring system that can protect your entire attack surface dynamically by detecting any suspicious behaviors.”