Organizations face operational deficiencies as they deal with hybrid IT complexities
While enterprises are taking advantage of cloud computing, all enterprises have on-going data center dependencies, a Pulse Secure report reveals.
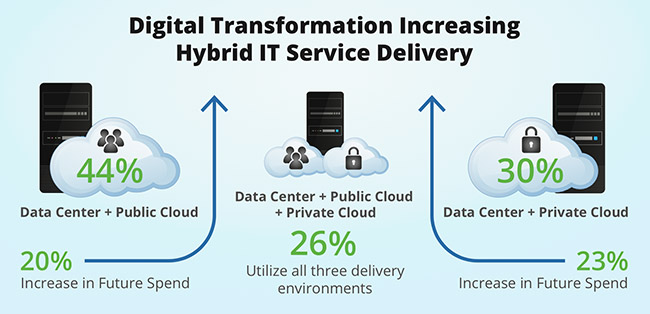
One fifth of respondents anticipate lowering their data center investment, while more than 40% indicated a material increase in private and public cloud investment.
According to the “2019 State of Enterprise Secure Access” report, “the shift in how organizations deliver Hybrid IT services to enable digital transformation must also take into consideration empowering a mobile workforce, supporting consumer and IoT devices in the workplace, and meeting data privacy compliance obligations – all make for a challenging environment to ensure, monitor and audit access security.
“What was consistent across enterprise sizes, sectors, or location was that secure access for hybrid IT is a current and growing concern with cyber threats, requirements and issues emerging from many sources.
“The reporting findings and insights should empower corporate leadership and IT security professionals to re-think how their organizations are protecting resources and sensitive data as they migrate to the cloud,” said Martin Veitch, editorial director at IDG Connect.
Security confidence
The survey found the most impactful incidents were contributed by a lack of user and device access visibility and lax endpoint, authentication and authorization access controls. Over the last 18 months, half of all companies dealt with malware, unauthorized/vulnerable endpoint use, and mobile or web apps exposures.
Nearly half experienced unauthorized access to data and resources due to insecure endpoints and privileged users, as well as unauthorized application access due to poor authentication or encryption controls.
While a third expressed significant confidence, 61% of respondents indicated modest confidence in their security processes, human resources, intelligence and tools to mitigate access security threats. The survey revealed the top access threat mitigation deficiencies:
- Defining app, data and resource access and protection requirements
- Defining, implementing and enforcing user and device access policy
- Provisioning, monitoring and enforcing BYOD and IoT device access
Operational gaps
When survey participants were asked what they perceive as their largest operational gaps for access security, the majority identified hybrid IT application availability; user, device and mobile discovery and exposures; weak device configuration compliance; and inconsistent or incomplete enforcement.
Correspondingly, the participants stated that their organizations are stepping up their access security initiatives:
- 48% improving endpoint security, remediation prior to access
- 46% enhancing IoT discovery, isolation and access control
- 44% fortifying network and cloud access visibility and resource segmentation
Zero Trust model
The cited incidents, threat mitigation deficiencies and operational gaps are among reasons for the interest in a Zero Trust approach for access security. A Zero Trust model authenticates, authorizes and verifies users, devices, applications and resources no matter where they reside.
It encompasses proving identity, device and security state before and during a transaction; applying a least privilege access closest to the entities, applications and data; and extending intelligence to allow policies to adapt to changing requirements and conditions.
Adding to management complexity, the report also found that organizations employ three or more secure access tools per each of 13 solutions presented in the survey. Larger companies have about 30% more tools than smaller enterprises.
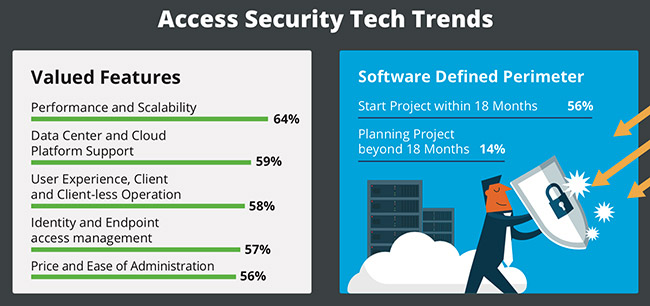
Correspondingly, nearly half of respondents were open to exploring the benefits of consolidating their security tools into suites. With the migration to cloud, one tool of interest cited by respondents as being implemented or planned over the next 18 months is Software Defined Perimeter (SDP).
Research highlights
- 91% of enterprises plan to increase secure access expenditure over the next 18 months; 30% anticipate an increase spend between 15% to 25%
- 44% of enterprises use data center in conjunction with public cloud, 30% in conjunction with private cloud, and 26% utilize all three delivery environments
- 46% of large enterprises prefer data center and private cloud; primarily preferred by Financial Services and U.K.-based companies
- 49% or more cited significant access incidents due to malware, unauthorized and vulnerable endpoint use, and mobile and web app exposures – healthcare organizations experienced greater mobile and web app exposures
- 81% expressed gaps in hybrid IT application availability – financial service experienced the most business impact related to application availability
- 78% indicated need for greater visibility of users, endpoints and mobile devices; more evident in large enterprises and those in the DACH region
- 42% will focus on refining privileged user or service account-based access – a top priority in financial services and manufacturing
- 48% stated a willingness to explore secure access tool consolidation into suites
- 56% stated a project or pilot of Software Defined Perimeter technology over the next 18 months
- Over 38% of respondents outsource secure access capabilities to Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) with additional MSSP usage to grow by 10% by 2021
The independent research for the report, which offers key insights into the current access security landscape and the maturity of defenses, was conducted by IDG Connect.
Survey respondents included more than 300 information security decision makers in enterprises with more than 1,000 employees across U.S., U.K. and DACH regions, and covered key verticals including financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, and services.