Which security practices lead to best security outcomes?
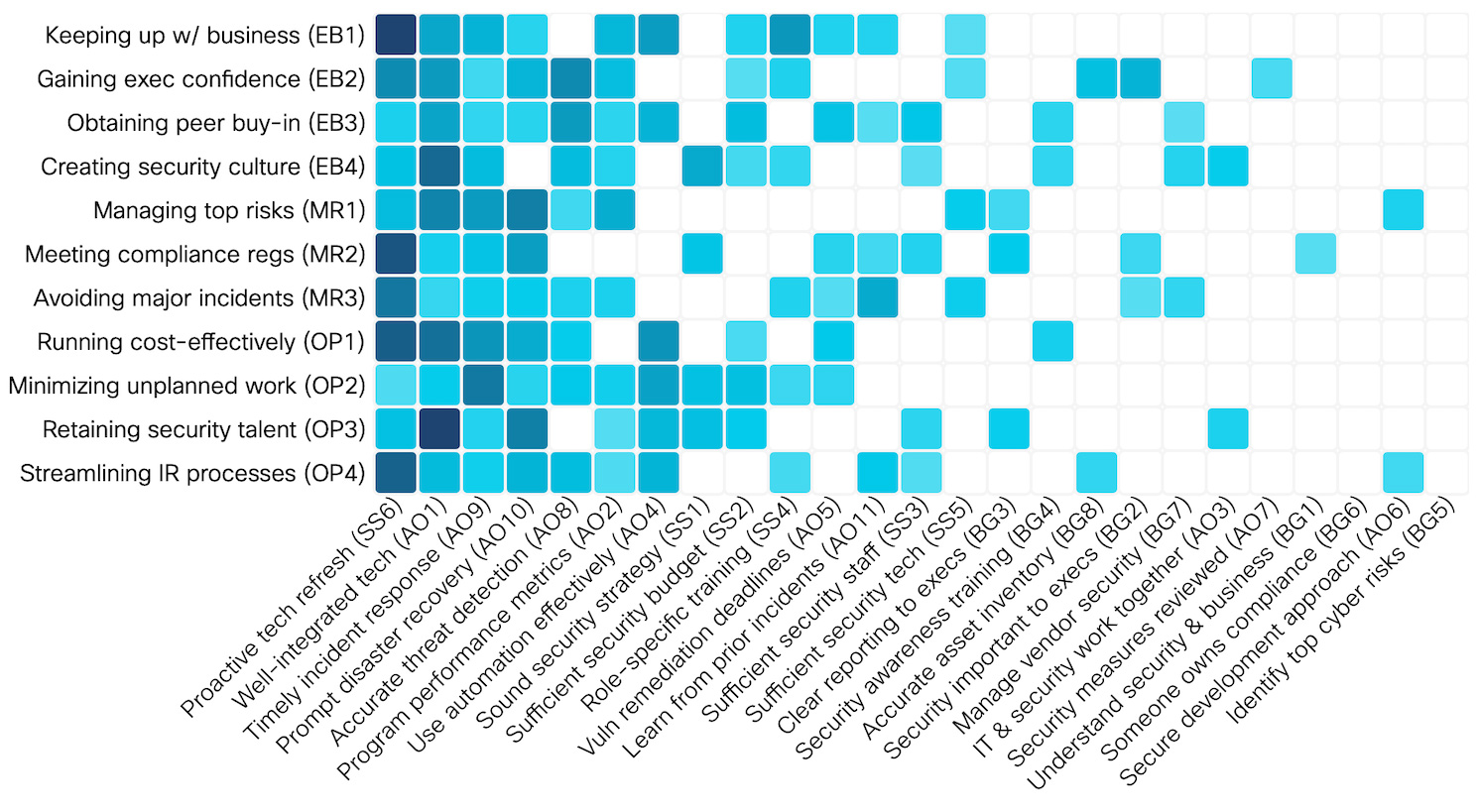
A proactive technology refresh strategy and a well-integrated tech stack are, according to a recent Cisco report, two security practices that are more likely than many others to help organizations achieve goals such as keeping up with business, creating security culture, managing top risks, avoiding major incidents, and so on.
A well integrated IT and security tech stack is a practice that is most conducive to retaining security talent, creating a security culture, and running cost-effectively, while a proactive tech refresh strategy will (most prominently) help achieve business goals, meet compliance regulations, avoid major incidents, and streamline IR processes.
Additional findings
Cisco’s report is based on a double-blind study that polled over 4,800 active IT, security, and privacy professionals from 25 countries around the world.
The analysis of the results revealed many expected and unexpected things:
- Identifying top cyber risks and having someone in the company who “owns” the compliance function (i.e., has “compliance” in the job title) does not correlate with any of the wanted outcomes.
- A well-integrated tech stack improves recruitment and retention of security talent.
- A strong security culture embraced by all employees depends on good equipment, a clearly communicated and sound security strategy, and timely fixes when things break.
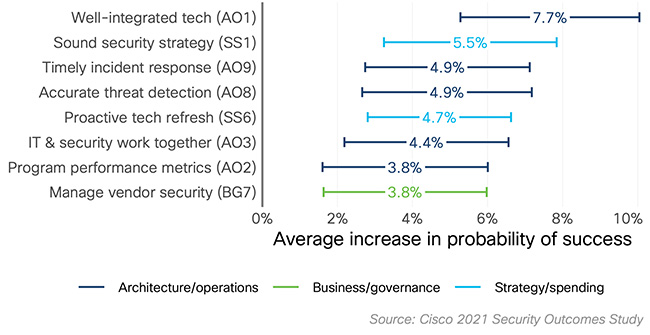
- Major incidents and losses can be avoided by proactively refreshing the technology used and by learning from prior incidents, through prompt disaster recovery, sufficient security tech, timely incident response and accurate threat detection.
- The effective use of automation helps companies keep up with business, run cost-effectively, minimize unplanned work, retain security talent and streamline IR processes, but does not correlate with meeting compliance regulation or avoiding major incidents.
- Organizations that successfully minimized the impact of COVID-19 on operations maintained a modern IT and security infrastructure, had adequate security staffing levels and invested in role-based training, and kept top executives informed.
- Meeting and maintaining compliance is the goal that’s easiest to achieve, while minimizing unplanned work is the hardest.
The most important success factors
In general, proactive tech refresh, well-integrated tech timely incident response and prompt disaster recovery significantly contribute to nearly every security outcome. Other practices may correlate to one or two specific outcomes or to all, but to a lesser extent.
“Beyond adherence to specific practices, we also asked respondents about where their security programs place the greatest priority in terms of investment, resources, and effort. We used the high-level security functions defined in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) for this,” the company noted.
“While the CSF’s Protect function isn’t at the bottom for every outcome, it ranks next to last for contributing to the overall success of the security program (Identify ranks #1). That’s certainly counterintuitive, but we don’t see this as suggesting protection isn’t important. Rather, it indicates that the best programs invest in a well-rounded set of defenses to identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from cyber threats. The field has long been protection-heavy; this says that protection alone is not the most effective strategy.”
The company has also published individual reports that cover various regions and the healthcare and financial services sectors