Businesses express concerns around ethical risks for their AI initiatives
Businesses are entering a new chapter in AI implementation where early adopters may have to work harder to preserve an edge over their industry peers, according to Deloitte.

The study shows that companies at the top will be those that utilize AI to pursue creative and novel applications, actively address inherent AI risks and — as more organizations buy AI-powered capabilities — become smarter consumers of AI technology.
“Seasoned” adopters are the example to follow as the global survey of 2,737 information technology and line-of-business executives finds this category has undertaken many AI production deployments. They have also developed a high level of AI expertise across the board in selecting AI technologies and suppliers; identifying use cases for building and managing AI solutions; integrating AI into their IT environment and business processes; and hiring and managing AI technical staff.
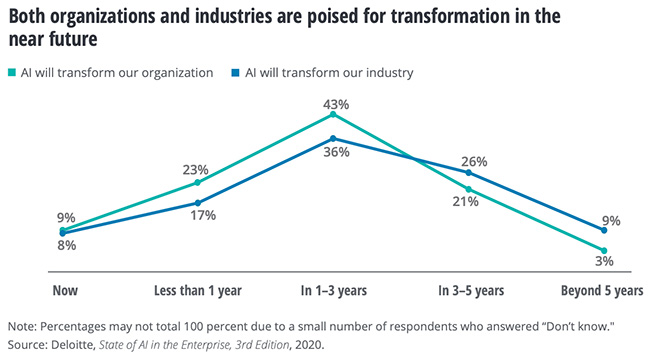
Seasoned and skilled adopters evolve
Responding organizations were grouped into three segments, based on the number of AI production deployments undertaken and how respondents rated their enterprise’s expertise across various measures.
- Seasoned adopters are setting the pace in terms of AI adoption maturity. This category of adopters has grown since the last survey in 2018 from 21% to 26%.
- Skilled adopters have generally launched multiple AI production systems but are not yet as AI-mature as the Seasoned organizations. This category of adopters has grown since the last survey from 43% to 47%.
- Starters are just dipping their toes into AI adoption and have not yet developed solid proficiency in building, integrating and managing AI solutions. This category of adopters has declined since the last survey from 36% to 27%.
“As organizations become more invested in AI, it is imperative that they have a common framework, principles and practices for the board, C-suite, enterprise and third-party ecosystem to proactively manage AI risks and build trust with both their business and customers,” said Irfan Saif, principal and AI co-leader, Deloitte & Touche.
”Our study results show that while early adopters of AI are still bullish, their competitive advantage may be waning as barriers to adoption continue to fall and more creative use of the technology grows.
“In the era of pervasive AI, where capabilities are readily available, organizations should go beyond efficiency and push boundaries to create new AI-powered products and services to be successful.” — Nitin Mittal, principal and AI co-leader, Deloitte Consulting.
Purchasing AI intelligently
As purchasing barriers have dropped and AI is more available, choosing the right technology is more important than ever. Those AI adopters surveyed tend to “buy” their capabilities rather than “build” them.
To become smarter consumers, companies should evaluate the landscape, find the most advanced AI and integrate those technologies into their infrastructure. However, the survey found many adopters lack purchasing maturity:
- Only 47% of all adopters say that they have a high level of skill around selecting AI technologies and technology suppliers.
- 45% say that they have a high level of skill around integrating AI technology into their existing IT environment.
Moving AI applications beyond IT and cyber security
It will likely take more creativity for organizations to differentiate themselves as AI becomes commonplace. For example, many companies are still using AI mostly in IT- and cybersecurity- related functions, which was also the case in Deloitte’s second edition of the survey. This year’s survey found:
- Forty-seven percent of respondents indicated that IT was one of the top two functions for which AI was primarily used.
- When asked to identify the top two benefits they were seeking from AI, respondents’ top choices were “making processes more efficient” and “enhancing existing products and services,” the same as the last survey.
- Top business functions for AI applications, such as marketing, human resources, legal and procurement ranked at the bottom of the list.
- However, there are signals that AI may be expanding as respondents rated “creating new products and services” as the third-highest overall AI benefit.
Managing risks: Advocating for trustworthy AI
Despite strong enthusiasm for their AI efforts, the majority of adopters only feel somewhat prepared to address AI risks — from unintended bias to determining accountability — and not enough are implementing specific practices to address them. In fact, survey respondents rank managing AI-related risks as the top challenge for their AI initiatives.
Adding to this trust concern, many adopters feel underprepared and that these risks may impede their AI efforts:
- More than half of adopters surveyed report “major” or “extreme” concerns about potential risks for their AI initiatives, while only four in 10 adopters rate their organization as “fully prepared” to address them.
- While cybersecurity remains the most worrisome AI risk for adopters, AI failures, misuse of personal data, and regulatory uncertainty are also top areas of concern.
- Fifty-six percent agree that their organization is slowing adoption of AI technologies because of the emerging risks, and the same proportion believe that negative public perceptions will slow or stop adoption of some AI technologies.
- Fifty-seven percent of adopters have “major” or “extreme” worries about how new and changing regulations could impact their AI initiatives.