Researchers analyzed 16.4 billion requests to see how bots affect e-commerce
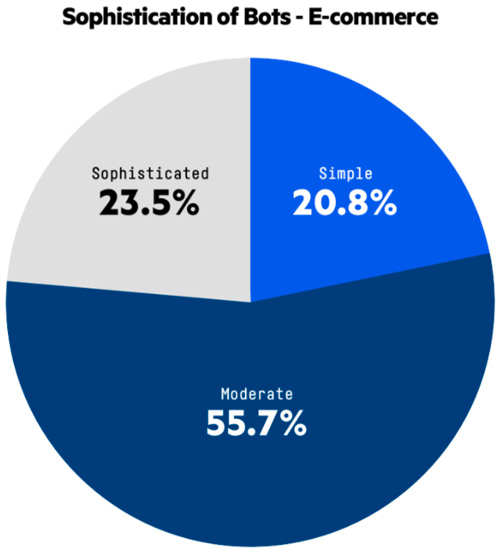
The sophistication level of bots attacking e-commerce sites is on the rise, with nearly four-fifths (79.2 percent) classified as moderate or sophisticated, up from 75.8 percent in 2018, according to the Imperva report.
The report analyzed 16.4 billion requests from 231 domains during the month of July 2019.
E-commerce companies suffer from a continual barrage of bad bots that criminals, competitors, resellers and investment companies use to carry out unauthorized price scraping, inventory checking, denial of inventory, scalping, customer account takeover, gift card abuse, spam comments, transaction fraud and more.
These nefarious activities not only damage the customer experience and brand, they can also lead to poor website performance and even downtime, ultimately resulting in lost revenue during peak traffic times like Black Friday and Cyber Monday.
“This study shows that bad bots cause round-the-clock damage on e-commerce websites, APIs and mobile apps,” said Tiffany Olson Kleemann, VP of Bot Management at Imperva and former CEO of Distil.
“We agree with the approach taken in proposed legislation to ban the use of ‘Grinch bots’ and ‘sneaker bots,’ which are used to scalp limited edition, high-demand inventory, yet we know from first-hand experience that legal action alone is not enough.
“Online retailers must also practice good web security hygiene and take advantage of the technology solutions at their disposal to protect their websites and customers. Gaining a granular understanding of bot threats is a critical first step in the right direction.”
Key findings
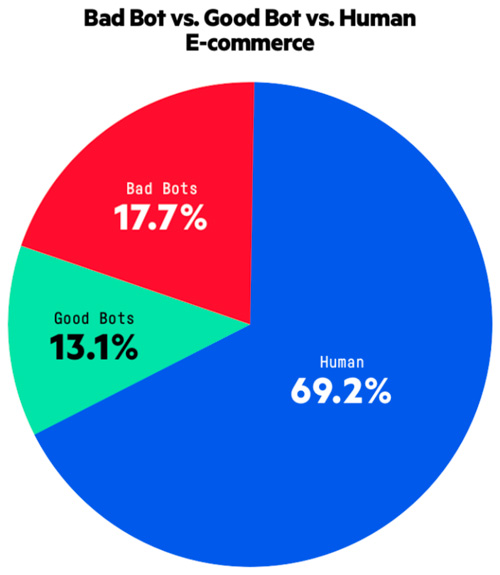
Bad bots, good bots and humans: E-commerce traffic consists of 17.7 percent bad bots, 13.1 percent good bots and 69.2 percent humans.
Sophistication level: Bad bots on e-commerce sites are becoming more advanced and difficult to detect. Nearly four-fifths (79.2 percent) are classified as moderate or sophisticated, up from 75.8 percent in 2018, while those classified as simple decreased from 24.2 to 20.8 percent. The rise in sophistication is due to the arms race at play between bot operators and bot mitigation technology.
Variety of attacks: The variety of bot attacks is more diverse in e-commerce than in many other industries. These attacks include unauthorized price and content scraping, denial of inventory, scalping by resellers, customer account takeover, credit card fraud and gift card fraud.
Country of origin: The top five countries from which e-commerce bad bots originate are the U.S. (63.6 percent), Germany (10.1 percent), France (6.2 percent), Canada (5.5 percent) and China (4.9 percent). Each country contributes a higher proportion of bad bot traffic on e-commerce sites compared to other industries.
Browser impersonation: The top five browsers that e-commerce bad bots use to mask their identities are Chrome (66 percent), Firefox (13.6 percent), Safari (6.8 percent), SEMRush (4.9 percent) and Android Webkit (2.2 percent), illustrating that the majority of e-commerce bots are attempting to hide in plain sight by impersonating the most popular browsers.