Defining and securing the Internet of Things
The EU Cybersecurity Agency ENISA published a report on the security of the Internet of Things (IoT). The study aims to set the scene for IoT security in Europe. It serves as a reference point in this field and as a foundation for relevant forthcoming initiatives and developments.
IoT threats impact
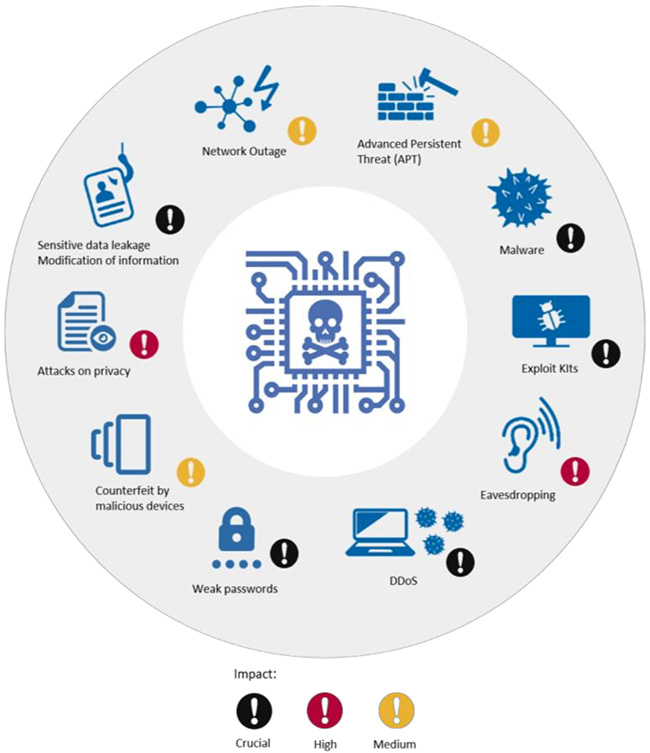
Security recommendations crucial for functionality
ENISA defines IoT as “a cyber-physical ecosystem of interconnected sensors and actuators, which enables intelligent decision making”. IoT brings the smart element into every life aspect of Europeans, from smart cars and wearables to smart grids and infrastructures. The threats and risks related to IoT devices, systems and services are growing, and new attacks are covered by the media every day.
“The deployment of IoT will be key to our smart cities, smart airports, smart health and smart X. It is envisaged, that IoT will be deployed everywhere and will have a positive impact on our lives. The deployment of baseline security recommendations into our IoT ecosystem will be critical to the proper function of these devices by mitigating and preventing cyber-attacks.”, said Prof. Dr. Udo Helmbrecht, Executive Director of ENISA.
Extremely complex landscape
With a great impact on citizens’ safety, security and privacy, the IoT threat landscape is extremely complex. Therefore, it is important to understand what exactly needs to be secured and to implement specific security measures to protect the IoT from cyber threats. This is particularly important in the context of ICT systems, which are either critical infrastructures themselves or essential for the operation of critical infrastructures.
The recommendations of the report are meant to be of use to all actors involved, from the European Commission and governments to the IoT industry, providers, operators, manufacturers and consumers’ associations.
IoT administration system compromised
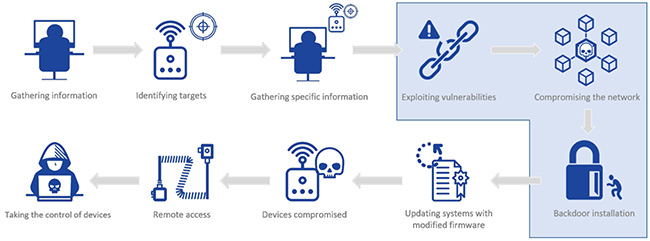
IoT is entering into all aspects all life so there is a need for a strong holistic approach and to:
- Promote harmonization of IoT security initiatives and regulations
- Raise awareness of the need for IoT cybersecurity
- Define secure software and hardware development lifecycle guidelines for IoT
- Achieve consensus on interoperability across the IoT ecosystem
- Foster economic and administrative incentives for IoT security
- Establishment of secure IoT product/service lifecycle management
- Clarify liability among IoT stakeholders.