Application downtime costing enterprises $16 million each year
Despite numerous high-profile incidents in the last year, enterprises are still not paying enough attention to the needs of their users, according to Veeam.
84 percent of senior IT decisions-makers (ITDMs) across the globe admit to suffering an availability gap (the gulf between what IT can deliver and what users demand). This costs businesses up to $16 million a year in lost revenue and productivity, in addition to the negative impact on customer confidence and brand integrity (according to 68 percent and 62 percent of respondents respectively).

This figure has risen $6 million in 12 months, despite almost all respondents saying that they have implemented tightened measures to reduce availability incidents and that 48 percent of all workloads classified as ‘mission-critical (rising to 53 percent by 2017).
With predictions there will be almost 21 billion connected devices by the end of 2020, the need to deliver 24/7 access to data and applications has never been more important. However, it seems that enterprises have not received that message despite more than two-thirds of respondents stating that they have invested heavily in data center modernization specifically to increase availability levels.
Availability is of paramount importance, yet enterprises are failing
- Users want support for real-time operations (63 percent) and 24/7 global access to IT services to support international business (59 percent).
- When modernizing their data centers, high-speed recovery (59 percent) and data loss avoidance (57 percent) are the two most sought-after capabilities; however, cost and lack of skills is inhibiting deployment.
- Organizations have increased their service level requirements to minimize application downtime (96 percent of organizations have increased the requirements) or guarantee access to data (94 percent) to some extent over the past two years, but the Availability Gap still remains.
- To address this, however, respondents stated that their organizations are currently, or are intending in the near future, to modernize their data center in some way – virtualization (85 percent) and backups (80 percent) are among the most common areas to update for this purpose.
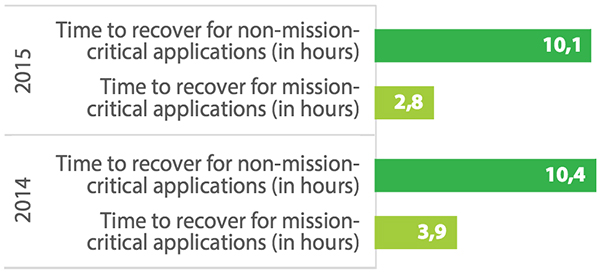
Data at risk
- SLAs for recovery time objectives (RTOs) have been set at 1.6 hours, but respondents admit that in reality recoveries take 3 hours. Similarly, SLAs for recovery point objectives (RPOs) are 2.9 hours, whereas 4.2 hours is actually being delivered. Respondents report that their organization, on average, experiences 15 unplanned downtime events per year. This compares to the average of 13 reported in 2014. With this, unplanned mission-critical application downtime length has increased from 1.4 hours to 1.9 hours year over year, and that non-mission-critical application downtime length has increased from 4.0 hours to 5.8 hours.
- Just under half only test backups on a monthly basis, or even less frequently. Long gaps between testing increase the chance of issues being found when data needs to be recovered – at which point it may be too late for these organizations. And of those that do test their backups, just 26 percent test more than 5 percent of their backups.
The financial impact
- As a result, the estimated average annual cost of downtime to enterprises can be up to $16 million. This is an increase of $6 million on the equivalent 2014 average.
- The average per hour cost of downtime for a mission-critical application is just under $80,000. The average per hour cost of data loss resulting from downtime for a mission-critical application is just under $90,000. When it comes to non-mission-critical applications, the average cost per hour is over $50,000 in both cases.
- Loss of customer confidence (68 percent), damage to their organization’s brand (62 percent), loss of employee confidence (51 percent) were the top three ‘non-financial’ results of poor availability cited.